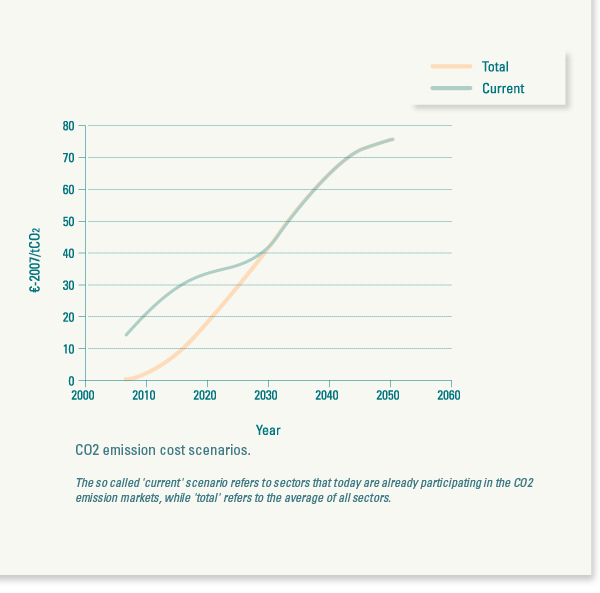
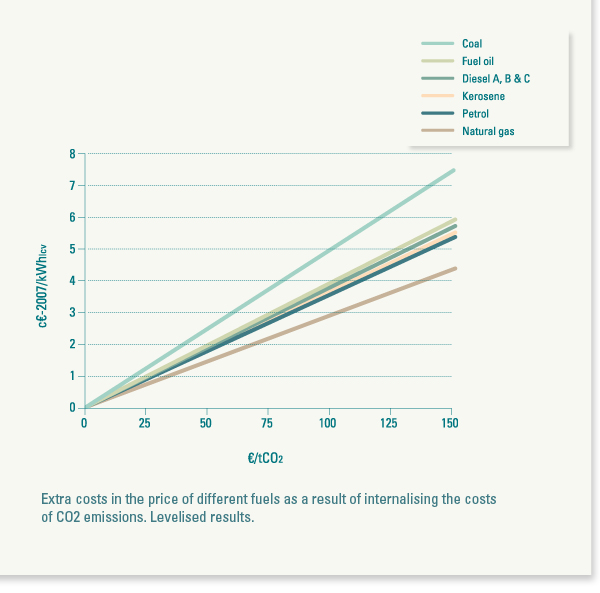
The adopted CO2 price scenarios have been elaborated bearing in mind three factors:
* Costs will tend to increase over time, as the requirements on emissions reduction became more stringent.
* All sectors responsible for emissions must join the emissions trading or incorporate other mechanisms (fees or taxes) to pay for the emitted CO2.
* CO2 prices in the market are expected to be below the costs of internalising the real impact of CO2 emissions.